Dams & Levees

Lincoln Lake Dam at Lincoln State Park.
Indiana has 1388 jurisdictional dams in the state. The Indiana Department of Natural Resources Dam Safety Program regulates the construction, operation and maintenance of Indiana’s dams to protect life and property from damages due to failure of dams. The program also assists with emergency preparedness activities.
Types of dams
A dam is a structure built across a stream, river or an estuary to store water. They serve many purposes such as recreation, water supply, flood control, sediment control and energy generation.
Types:
- Earthfill dams
- Rockfill dams
- Concrete dams
Most dams in Indiana are earthfill embankment dams.
Typical earthen dam
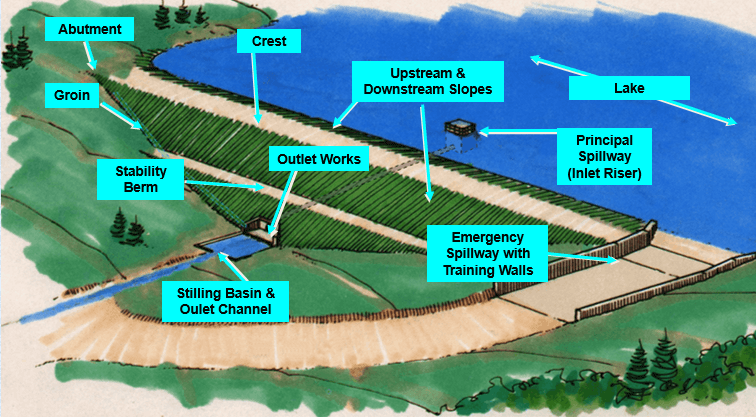
Image courtesy of Natural Resources Conservation Service, USDA.
The risk
Knowing and reducing the risks of dams can save lives and property. Dams most often fail during an extreme rainfall event due to unrecognized or unaddressed design or maintenance deficiencies.
Past Failures

Bean Blossom, Monroe County.
- Kelly Barnes Dam, Georgia, 1977
- Oroville Dam, California, 2017
- Edenville Dam and Sanford Dam, Gladwin and Midland counties, Michigan, May 20, 2020
- Prince’s Dam, Johnson County, Indiana, June 2008
- Bean Blossom, Monroe County, Indiana, November 1993
The Association of State Dam Safety Officials (ASDSO) offers a series of publications about Living With Dams. These e-booklets were created to help answer questions about dams: purposes they serve, risks associated with dams and where to get information about how to react if you are affected by a dam. The Indiana DNR Dam Safety Program is a member of the association.
Dams in Indiana
A dam is under Indiana DNR’s jurisdiction if it meets any of the following criteria:
- Has a drainage area above the dam of more than one square mile.
- Exceeds 20 feet in height.
- Impounds a volume of more than 100 acre-feet of water.
- High-hazard classification through successful petition by a downstream property owner.
Those that are federally owned and operated are not under Indiana’s jurisdiction.
Dams under jurisdiction are inspected by the Indiana DNR Dam Safety Program field staff or a private engineer approved by Indiana DNR every 2-5 years.
Hazard classification
A dam is assigned a hazard classification based on how much damage and loss of life that could occur if it fails. These classifications are assigned by Indiana DNR. The classification can change when downtream conditions change.
High hazard: The failure of a structure may cause the loss of life and serious damage to homes, industrial and commercial buildings, public utilities, major highways, or railroads.
- Number of high hazard dams in Indiana: 278.
- Example: Eagle Creek Reservoir dam in Marion county.
Significant hazard: The failure of a structure may damage isolated homes and highways, or cause the temporary interruption of public utility services.
- Number of significant hazard dams in Indiana: 321.
- Example: Glendale Reservoir Dam in Daviess County.
Low hazard: The failure of a structure may damage farm buildings, agricultural land, or local roads.
- Number of low hazard dams in Indiana: 789.
- Example: Broad Ripple Dam in Marion County.
Dam ownership
All dams, including dams that fall under Indiana DNR jurisdiction, should be operated and maintained in a safe manner. Under Indiana law (IC 14-27-7.5-7), the owner of a structure is required to maintain and keep the structure in safe operating condition.
Own a Dam?



