Main Content
Article
File a Complaint
How to File A Complaint
The Indiana Professional Licensing Agency and each of its boards and commissions is charged with the responsibility of disciplining license holders who have violated practice standards, acted dishonestly, or acted unethically. Indiana has standards of practice that apply to all regulated professions. Those standards, along with laws and rules specific to each profession, provide the basis upon which boards impose discipline on licensed professionals.
It is never our intention to inhibit the practice of business in Indiana. However, in the unfortunate situation where the Indiana Attorney General seeks action in a case, it is our duty to comply with the highest standards of fairness, justice and uphold the laws that keep Hoosiers safe.
To file a complaint with the Indiana Attorney General click here for the form.
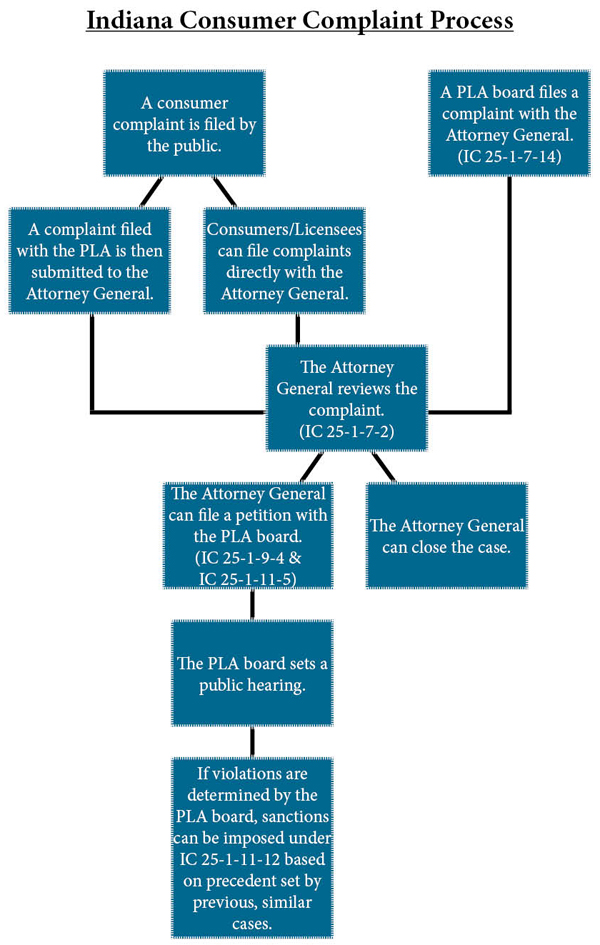
How the Process Works
A consumer complaint can be filed with the Indiana Professional Licensing Agency or directly to its ultimate home, the Indiana Attorney General. Either way, the first step for any complaint is a review by the Attorney General. If evidence is found to suggest the complaint has merit, the Attorney General then brings it to the appropriate board or commission, seeking action against the license holder. (This step is much like a prosecutor who believes he has a case to take to court; in this situation, the Attorney General ‘tries the case’ before the respective board or commission, which acts like a judge). It is the Attorney General, then, who decides to seek disciplinary action. Once the Attorney General pursues the case it is the board or commission that holds a hearing and determines the outcome, including disciplinary actions.
The complaint names the State of Indiana as the petitioner and the attorney general, through a deputy attorney general, represents the state. The complaint describes the alleged conduct the professional, referred to as the respondent, has engaged in and the standards of practice the professional has allegedly violated unless it is a complaint for a summary suspension. Complaints for summary suspension often include only a general statement of facts alleging that a professional represents a clear and immediate danger to the public health and safety if the professional is allowed to continue to practice.
Disciplinary hearings are held before the board or an administrative law judge appointed by the board. A case may be resolved through a settlement agreement, in which case there will be no evidentiary hearing. After a hearing, the board will deliberate and make its findings of fact and conclusions of law, and then the board decides the appropriate disciplinary sanction, if any, to impose on the professional's license. The possible sanctions are: revocation, suspension, probation, censure, reprimand, or a combination of these. The boards also have the authority to impose a fine in an amount not to exceed $1,000 for each violation of law, except for a finding of incompetence due to a physical or mental disability.
Commonly Used Terms
Administrative Complaint - a complaint filed with the board by the Attorney General that describes the alleged conduct a licensed professional has engaged in and the laws and administrative rules the professional has violated; sometimes referred to as disciplinary charges.
Administrative Law Judge - an individual or panel of individuals that preside over an administrative proceeding, receive the evidence, and make a decision.
Censure - an expression of official disapproval that is an official record that the license has been disciplined. The censure itself does not affect the status of the license or the licensee's ability to practice. The censure may be imposed in combination with other types of disciplinary sanctions. A censure and a reprimand are similar.
Conclusions of Law - the conclusions the board reaches by applying the facts of a case to the relevant law.
Consumer Complaint - a complaint filed by a member of the public against a licensed professional. To obtain a complaint form, go to http://www.indianaconsumer.com/.
Default - omission, neglect, or failure of a party to take a step required, such as failing to appear for a hearing.
Disciplinary Charges - a complaint filed with the board by the Attorney General that describes the alleged conduct a licensed professional has engaged in and the laws and administrative rules the professional has violated; sometimes referred to as an administrative complaint.
Emergency Suspension - a 90-day suspension of a licensed professional's license after a finding that a professional represents a clear and immediate danger to the public health and safety if the professional is allowed to continue to practice; also called a summary suspension.
Final Order - the written order issued by the board following an administrative hearing that contains the findings of fact and conclusions of law in the case.
Findings of Fact - the facts that the board determines have been proven in an administrative hearing on a disciplinary complaint.
Probation - professionals whose licenses are placed on probation are allowed to continue practicing subject to certain terms and conditions. The conditions imposed as part of an order of probation will vary depending on the circumstances of the case.
Reprimand - a reprimand is an official record that the license has been disciplined. The reprimand itself does not affect the status of the license or the licensee's ability to practice. The reprimand may be imposed in combination with other types of disciplinary sanctions. A reprimand and a censure are similar.
Respondent - the professional against whom disciplinary charges are brought.
Revocation - professionals cannot practice with a revoked license. The professional cannot apply for a new license for seven years from the date of the revocation.
Settlement Conference - a meeting conducted with the parties in a case conducted by a board member or ALJ to discuss settling the case as an alternative to having a contested hearing.
Summary Suspension - a 90-day suspension of a professional's license based upon a finding that the professional represents a clear and immediate danger to the public health and safety if allowed to continue to practice; also called an emergency suspension.
Suspension - professionals whose licenses have been suspended cannot practice during the period of suspension. Suspensions are typically imposed for an indefinite period of time with the board setting the minimum time that must pass before the professional can apply for reinstatement of the suspended licenses. In many cases, the suspension is followed by a period of probation.
Do You Have a Customer Dispute?
Do you have a dispute with a company or a provider that might lead to your getting a resolution on the product or service you purchased? The Better Business Bureau supports consumers and businesses alike, and it sets standards for ethical business behavior and monitors compliance.
Click here to file a complaint. They will review your marketplace dispute and serve as a liaison between you and the business to provide a fair process with an equitable outcome. This is a marketplace solution, not a legal one. It is similar to a mediator working with you and the company where you might seek a refund or a better service from that company. Note: The Better Business Bureau does not consider workplace disputes, discrimination claims, matters that are or have been litigated or claims about the quality of health or legal services.
